Linq
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
select x).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
where
x.EID==1 && x.NAME=="A"
select x).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
where
x.EID==2 || x.NAME=="A"
select x).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
where
x.EID!=2
select x).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
orderby x.EID descending
select x).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
group
x by x.DID into z
select new {z.Key,Count=z.Count()}).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
let
y=(x.DID==1?"Siv":x.DID==2?"Sankar":"Mahadev")
select new {x.NAME,y }).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
join
y in obj.DEPTs
on
x.DID equals y.DID
select new {x.NAME,y.DID }).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
join
y in obj.DEPTs
on
x.DID equals y.DID
into
z
from
y in z.DefaultIfEmpty()
select new {x.NAME,y.DNAME }).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
join
y in obj.EMPs
on
x.MGR equals y.EID
select new {name=x.NAME+" Is Working Under "+y.NAME }).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
from y in obj.DEPTs
where 1==1
select new {x.NAME,y.DNAME }).ToList();
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
from y in obj.DEPTs
from z in obj.SALGRADEs
where x.DID==y.DID && (x.SALARY>=z.LOWSAL &&
x.SALARY<=z.HISAL)
select new {z.SID,x.NAME,y.DNAME }).ToList();
var m = obj.EMPs.Where(x => x.DID == 3);
var n =
obj.EMPs.Union(m).ToList();
var m = obj.EMPs.Where(x => x.DID == 3);
var n =
obj.EMPs.Intersect(m).ToList();
var m = obj.EMPs.Where(x => x.DID == 3);
var n =
obj.EMPs.Except(m).ToList();
example of subquery
var m = (from x in obj.EMPs
where obj.EMPs.Any(y => x.MGR == (obj.EMPs.FirstOrDefault(n =>
n.NAME == "A")).EID)
select x).ToList();
example of SelectMany
public class DEPTVM
{
public int DID { get; set; }
public string DNAME { get; set; }
public List<EMP> ELIST { get; set; }
}
using (Database1Entities obj = new Database1Entities())
{
List<DEPTVM> m = obj.DEPTs.Select(n => new
DEPTVM { DID = n.DID, DNAME = n.DNAME, ELIST = obj.EMPs.Where(p=> p.DID ==
n.DID).ToList() }).ToList();
var n = m.SelectMany(p=>p.ELIST).ToList();--here
we can fetch all employee records.
m.Where(q=>q.DID==2).SelectMany(p=>p.ELIST).ToList();--here we can fetch
all employee which is working on department 2.
}
--------------------------------------------------
Function
Scalar value function
Create function fx(@sd datetime)returns varchar(50)
as
begin
return replace(convert(varchar,@sd,106),' ','-')
end
select dbo.fx(GETDATE())
Table value function
Create function fx() returns table
return(select * from emp)
select * from dbo.fx()
Inline function
Create function fx(@sd datetime,@ed datetime)returns @tb table(cdate varchar(50),statu varchar(50))
as
begin
while @ed>=@sd
begin
insert into @tb values(REPLACE(convert(varchar,@sd,106),'-',' '),DATENAME(dw,@sd))
set @sd=DATEADD(day,1,@sd)
end
return
end
select * from dbo.fx(GETDATE(),DATEADD(day,30,GETDATE()))
Store Procedure
create procedure sp_Test
as
begin
DECLARE @eid int,@name varchar(50),@sal money,@C_test cursor
create table #tb
(
EID INT,
NAME NVARCHAR(50),
SAL MONEY,
TA MONEY
)
set @C_test = cursor for select eid,name,sal from EMP
open @C_test
fetch @C_test into @eid,@name,@sal
while @@FETCH_STATUS=0
begin
insert into #tb values(@eid,@name,@sal,(@sal*.1))
fetch @C_test into @eid,@name,@sal
end
close @C_test
deallocate @C_test
select * from #tb
end
exec sp_Test
DML Trigger
create trigger t on emp1 for insert,update,delete
as
begin
declare @i int,@d int
select @i=COUNT(*) from inserted
select @d=COUNT(*) from deleted
if @i>0 and @d=0
insert into EMP2 select eid,name,GETDATE(),'INSERT' from inserted
else if @i=0 and @d>0
insert into EMP2 select eid,name,GETDATE(),'DELETE' from deleted
else if @i>0 and @d>0
begin
insert into EMP2 select eid,name,GETDATE(),'OLD' from deleted
insert into EMP2 select eid,name,GETDATE(),'NEW' from inserted
end
end
Instead of Trigger
create trigger t on v instead of insert
as
begin
insert into EMP3 select eid,name,sal,(sal*1) from inserted
end
Here 'v' is a view.
CTE
With cte as(select *,DENSE_RANK() over(order by sal desc) as POSITION from emp) select * from cte where POSITION=2
Query
select * from EMP
select * from EMP where EID=1 and NAME='A'
select * from EMP where EID=2 or NAME='A'
select * from EMP where EID!=2
select distinct did from EMP
select top(1) * from EMP
select * from emp where sal between 80000 and 100000
select * from EMP order by EID asc
select * from EMP order by EID desc
select * from emp where sal like '1%'
select did,count(*) from EMP group by DID having COUNT(*)>1
select E.NAME,D.DNAME from EMP E inner join DEPT D on E.DID = D.DID
select E.NAME,D.DNAME from EMP E left join DEPT D on E.DID = D.DID
select E.NAME,D.DNAME from EMP E right join DEPT D on E.DID = D.DID
select E.NAME,D.DNAME from EMP E full join DEPT D on E.DID = D.DID
select E.NAME,D.DNAME from EMP E cross join DEPT D
select ISNULL(M.NAME,'')+' IS WORKING UNDER '+ISNULL(T.NAME,'') from EMP M JOIN EMP T ON M.MGR=T.EID
select ISNULL(M.NAME,'')+' IS WORKING UNDER '+ISNULL(T.NAME,'') from EMP M FULL JOIN EMP T ON M.MGR=T.EID
SELECT * FROM EMP E JOIN DEPT D ON E.DID =D.DID JOIN SALGRADE S ON E.SAL BETWEEN S.LOWSAL AND S.HISAL
SELECT * FROM EMP E,DEPT D,SALGRADE S WHERE E.DID=D.DID AND E.SAL BETWEEN S.LOWSAL AND S.HISAL
select * from emp where MGR=(select EID from EMP where NAME='A')
select * from emp where DID in(select DID from DEPT)
select *, case when did=1 then 'siv' when did=2 then 'sankar' else 'mahadev' end as Test from EMP
--------------------------------------------------------------------
declare @name nvarchar(max)=''
select @name=@name+','+name from Emps
select SUBSTRING(@name,2,LEN(@name))
Output
--------------------------------------------------------------------
How to update multiple records update in SQL
Using Stored Procedure & Cursor
Create procedure [SP_speedcode_entry]
(
@FMOserver nvarchar(100),
@SPEEDCODE nvarchar(50)
)
as
begin
declare @SCRIPTNAME nvarchar(max),@ENTRYPOINT int,@check nvarchar(50),@name nvarchar(max),@C_Speedcode_List cursor
BEGIN TRY
set @C_Speedcode_List =cursor for select SCRIPTNAME,ENTRYPOINT from speedcode_entry where SPEEDCODE=@SPEEDCODE
open @C_Speedcode_List
fetch @C_Speedcode_List into @SCRIPTNAME,@ENTRYPOINT
while @@FETCH_STATUS=0
begin
select @check=LTRIM(RTRIM(SUBSTRING(@SCRIPTNAME, 1,5) ))
if @check = 'https'
select @name=LTRIM(RTRIM(SUBSTRING(@SCRIPTNAME, 34,LEN(@SCRIPTNAME))))
else
select @name=LTRIM(RTRIM(SUBSTRING(@SCRIPTNAME, 33,LEN(@SCRIPTNAME))))
update speedcode_entry set SCRIPTNAME=LTRIM(RTRIM(@FMOserver))+@name where ENTRYPOINT=@ENTRYPOINT
fetch @C_Speedcode_List into @SCRIPTNAME,@ENTRYPOINT
end
close @C_Speedcode_List
deallocate @C_Speedcode_List
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
print 'This is the CATCH block within our Stored Procedure:'
+ ' Error Line #'+convert(varchar,ERROR_LINE())
+ ' and Error '+convert(varchar,ERROR_MESSAGE())
END CATCH
end
-- execute SP_speedcode_entry 'http://g7w02449a.inc.hpicorp.net','ELBU'
Using Common Table Expression
with CTE_Speedcode_Entry
AS
(
SELECT [SPEEDCODE],[ENTRYPOINT] ,case when SUBSTRING([SCRIPTNAME],1,5)= 'https' then LTRIM(RTRIM(SUBSTRING([SCRIPTNAME],34,LEN([SCRIPTNAME])))) else LTRIM(RTRIM(SUBSTRING([SCRIPTNAME],33,LEN([SCRIPTNAME])))) end AS OLDURL FROM [speedcode_entry]
where [SPEEDCODE]='ELBU'
)
UPDATE Speedcode_Entry SET Speedcode_Entry.[SCRIPTNAME]=LTRIM(RTRIM('http://g7w02439a.inc.hpicorp.net')) + CTE_Speedcode_Entry.OLDURL
from Speedcode_Entry , CTE_Speedcode_Entry
where Speedcode_Entry.[ENTRYPOINT]=CTE_Speedcode_Entry.[ENTRYPOINT]
Using Subquery
update speedcode_entry set SCRIPTNAME='http://g7w02448a.inc.hpicorp.net'+case when SUBSTRING(SCRIPTNAME,1,5)='https' then LTRIM(RTRIM(SUBSTRING(SCRIPTNAME,34,LEN(SCRIPTNAME)))) else LTRIM(RTRIM(SUBSTRING(SCRIPTNAME,33,LEN(SCRIPTNAME)))) end where ENTRYPOINT =any(select ENTRYPOINT from speedcode_entry where [SPEEDCODE]='ELBU')
Pass comma separated (delimited) values as Parameter to Stored Procedure in SQL Server
CREATE FUNCTION SplitString
(
@Input NVARCHAR(MAX),
@Character CHAR(1)
)
RETURNS @Output TABLE (
Item NVARCHAR(1000)
)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @StartIndex INT, @EndIndex INT
SET @StartIndex = 1
IF SUBSTRING(@Input, LEN(@Input) - 1, LEN(@Input)) <> @Character
BEGIN
SET @Input = @Input + @Character
END
WHILE CHARINDEX(@Character, @Input) > 0
BEGIN
SET @EndIndex = CHARINDEX(@Character, @Input)
INSERT INTO @Output(Item)
SELECT SUBSTRING(@Input, @StartIndex, @EndIndex - 1)
SET @Input = SUBSTRING(@Input, @EndIndex + 1, LEN(@Input))
END
RETURN
END
GO
Output
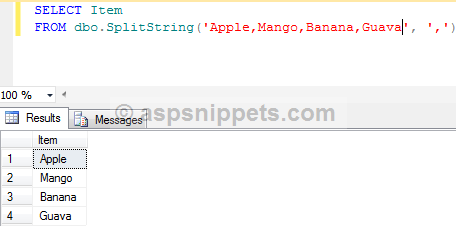
Using the Split String function in a Stored Procedure
The following stored procedure gets the records of Employees for which the Ids are passed using a string separated (delimited) by comma.
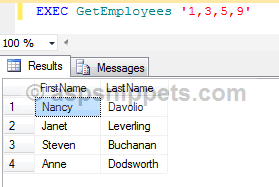
CREATE PROCEDURE GetEmployees
@EmployeeIds VARCHAR(100)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT FirstName, LastName
FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeId IN(
SELECT CAST(Item AS INTEGER)
FROM dbo.SplitString(@EmployeeIds, ',')
)
END
The stored procedure is executed as follows
EXEC GetEmployees'1,3,5,9'
Output
SQL
select case when xtype='F' then 'Foreign Key' end Keys ,count(*) 'Number Of Forigen Key' from sysobjects group by xtype having xtype='f'
select case when xtype='pk' then 'Primary Key' end Keys ,count(*) 'Number Of Primary Key' from sysobjects group by xtype having xtype='pk'
select case when xtype='uq' then 'Unique Key' end Keys ,count(*) 'Number Of Unique Key' from sysobjects group by xtype having xtype='uq'
select case when xtype='u' then 'Tables' end Tables ,count(*) 'Number Of Table' from sysobjects group by xtype having xtype='u'
select case when xtype='v' then 'views' end Tables ,count(*) 'Number Of Views' from sysobjects group by xtype having xtype='v'
select case when xtype='p' then 'Procedures' end [Procedures] ,count(*) 'Number Of Procedures' from sysobjects group by xtype having xtype='p'
SELECT TABLE_NAME,COUNT(COLUMN_NAME) 'Number Of Columns'
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS
group by TABLE_NAME
Having TABLE_NAME =any(select TABLE_NAME from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS)
select distinct t.name 'Table Name',SCHEMA_NAME(t.schema_id) 'Schema Name',i.rows 'Number Of Rows' from sysindexes i
join sys.tables t on i.id=t.object_id order by t.name
Using below query we can know free space and used space in SQL DB.
SELECT DB_NAME() AS DbName,
name AS FileName,
size/128.0 AS UsedSpaceMB,
size/128.0 - CAST(FILEPROPERTY(name, 'SpaceUsed') AS INT)/128.0 AS FreeSpaceMB
FROM sys.database_files; ORACLE
SELECT table_name FROM user_tables ORDER BY table_name
SELECT table_name, owner FROM all_tables where TABLE_NAME like 'ELF%';
SELECT * FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'PROCEDURE'
SELECT * FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'FUNCTION'
SELECT * FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'PACKAGE'
select * from all_constraints where r_constraint_name in(select constraint_name fromall_constraints where table_name like 'ELF_SALES_ORDER%')
C (check constraint on a table)
P (primary key)
U (unique key)
R (referential integrity)
V (with check option, on a view)
O (with read only, on a view)
----
select table_name, num_rows counter from all_tables where owner = 'owner' order by table_name;
-----
Tables: select * from tab;
Views: select object_schema_name(v.object_id) schema_name, v.name from sys.view as v;
Procedures: select * from information_schema.routines where routine_type = ‘PROCEDURE’;
Functions: : select * from information_schema.routines where routine_type = ‘function;
-----
select count(*) from SYS.ALL_TABLES where owner=' ';
select count(* ) from SYS.ALL_INDEXES where owner=' ';
select count(*) from user_constraints where owner=' ';
SELECT * FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE IN ('FUNCTION','PROCEDURE','PACKAGE') and owner=’’;
select view_name from all_views where owner='';
owner name is DB user.
oracle
select count(* ) AS Indexes from SYS.ALL_INDEXES
select count(*) AS “Primary Key” from all_constraints where CONSTRAINT_TYPE='P'
select count(*) AS “Check” from all_constraints where CONSTRAINT_TYPE='C'
select count(*) AS “Unique Key” from all_constraints where CONSTRAINT_TYPE='U'
select count(*) AS “Foreign Key” from all_constraints where CONSTRAINT_TYPE='R'
select table_name, num_rows as "Number Of Rows" from all_tables order by table_name;
select count(*) Views from SYS.ALL_VIEWS
SELECT COUNT(*) as Procedure FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'PROCEDURE'
SELECT COUNT(*) as "Functions" FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'FUNCTION'
SELECT COUNT(*) Packages FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'PACKAGE'
select count(*) from SYS.ALL_INDEXES where owner='xx'
select count(*) from all_constraints where CONSTRAINT_TYPE='C' and owner='xx'
select count(*) Views from SYS.ALL_VIEWS where owner='xx'
SELECT COUNT(*) as Procedure FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'PROCEDURE' and owner='xx'
SELECT COUNT(*) as "Functions" FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'FUNCTION' and owner='xx'
SELECT COUNT(*) Packages FROM ALL_OBJECTS WHERE OBJECT_TYPE = 'PACKAGE' and owner='xx'
select COUNT(*) from all_tables where owner='xx'
select table_name, num_rows as "Number Of Rows" from all_tables where owner='xx' order by table_name;
select * from ALL_JOBS where schema_user='xx'
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Transaction and Entity Framework 6
Entity Framework internally maintains a transaction when you call the SaveChanges() method. So all Inserts, update operations under a single save changes method call will be in a single transaction. But when you want to wrap multiple SaveChanges() methods under a single transaction there is not any built-in functionality in earlier versions of Entity Framework.
Now, with Entity Framework 6.0, we have two built-in APIs for transactions:
DbContext.Database.BeginTransaction
This API call will allow us to begin a transaction for multiple save changes. You can combine as many operations as you want under a single transaction and hence either all will be performed successfully then the transaction will be committed. If any exception occurs then the transaction will be rolled back.
DbContext.Database.UseTransaction
Some times we need to use a transaction which is started outside of the entity framework. In this case this API call allows us to also use that transaction with Entity Framework.
In this blog post, we are going to use Begin Transaction. In the future, I plan to write a separate blog post about how to use existing transaction with entity framework.
So enough theory, let's create a console application to understand it better.
In this application, we are going to use two model classes called category and product. We will save them both in single transaction and try to understand how transaction works with Entity Framework.
The category model is listed below:
Here is the product model:
Here you can see I have the category ID in Product an Product belongs to Category. I have created my dbcontext class as shown below:
The Main method of console application is displayed below, which illustrates a real scenario where an exception might occurs during multiple save changes().


